Coronavirus pandemics
- Immunology Hub
- 2 apr 2020
- Tempo di lettura: 1 min
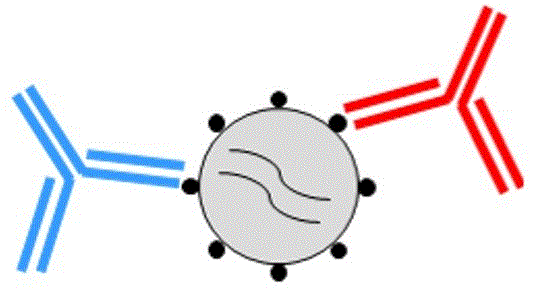
Coronaviruses are ssRNA viruses with with genome size of 26-32 kb. The infection process begins with viral binding to host cell receptors. A crucial glycoprotein on viral surface drives the fusion which finally results in the entry of the nucleocapsid into host cell cytoplasm. These early events are followed by the translation of the viral genome by host cell ribosomes. The proteins encoded by the viral genome are the spike protein, two large membrane proteins, an envelope protein and the nucleoprotein. Neutralizing antibodies (nAbs) preventing viral attachment, fusion or entry into the host cell might be considered for the development of a suitable vaccine for the recent Covid-19 outbreak.
#Immunology#coronavirus#science#genetics#immunology#medicine#medicalschool#research#socialdistancing#ppe#quarantine#virus#femalesinscience#femaleentrepreneur#yougotthis#selflove#selfcare#wegotthis#drebru#immunesystem#molecularmedicine#coronavir#biliminsan#bilimhayatkurtar#sciencesaveslives#covid19#stayhome#stayhealthy#staystrong#jenner





Commenti